"Am I becoming an alcoholic?" This question often signals a crucial moment of self-awareness. Alcoholism, clinically known as Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD), is a complex medical condition characterized by an impaired ability to control alcohol...


"Am I becoming an alcoholic?" This question often signals a crucial moment of self-awareness. Alcoholism, clinically known as Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD), is a complex medical condition characterized by an impaired ability to control alcohol...
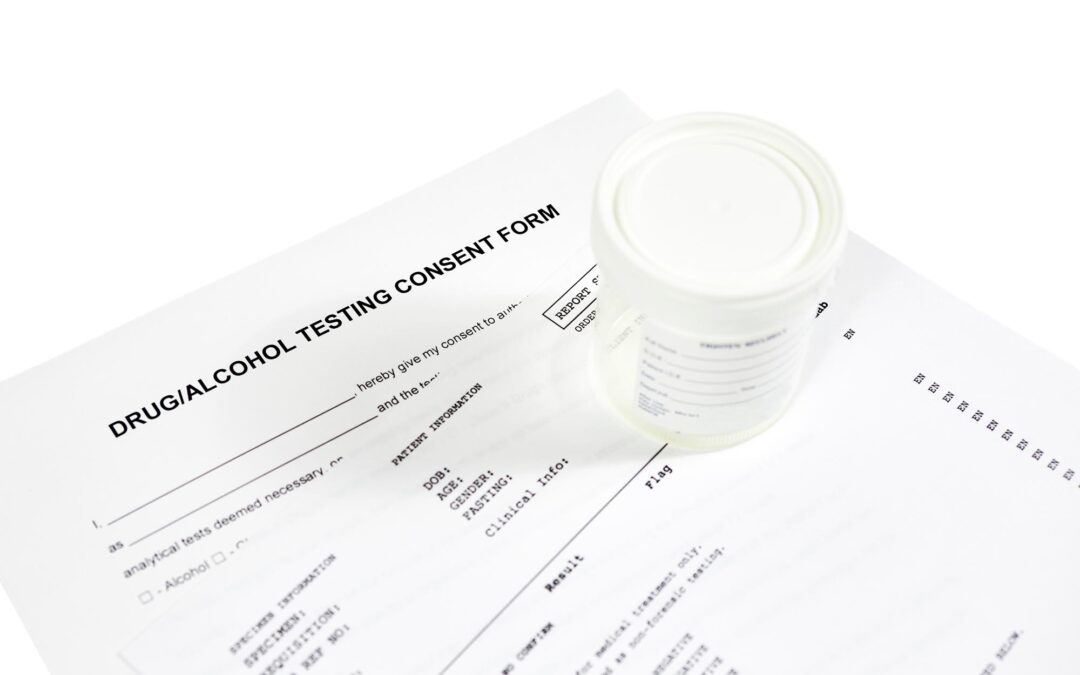
Understanding Alcohol Metabolism and Detection in Urine When you drink alcohol, your body begins processing it almost immediately using a complex metabolic system. The liver plays a central role in this process, utilizing specific enzymes to break...
Introduction The relationship between liquor marketing and consumer behavior reveals a complex web of influence that shapes drinking habits across society. Behind every carefully crafted alcohol advertisement lies a sophisticated strategy designed...

Introduction Azithromycin is one of the most prescribed antibiotics worldwide, treating a wide range of bacterial infections, from respiratory ailments to skin conditions. This powerful medication helps millions of people recover from infections...

Introduction Omeprazole is one of the most commonly prescribed medications in the United States. It is a powerful proton pump inhibitor (PPI) used to treat various digestive conditions. This medication works by reducing the production of stomach...

The Risks of Quitting Alcohol Cold Turkey: What You Need to Know Quitting alcohol cold turkey can be dangerous, especially for those with a history of heavy drinking or alcohol use disorder. This article explores the risks associated with abruptly...

Taking the first step toward recovery from alcohol addiction is undeniably a courageous act. If you or someone you love is struggling with ETOH (ethyl alcohol) dependence, then ETOH rehab can offer a safe, supportive, and structured environment....

Many people enjoy a drink or two on occasion. However, for some, social drinking can progress into a more serious problem known as alcoholism, also referred to as Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD). Signs of alcoholism can be subtle at first, but they can...

Alcohol abuse and depression are two serious health issues that often intertwine, creating a devastating cycle. If you or someone you love is struggling, understanding this connection is the first step towards recovery. The Complex Relationship:...

Updated 02/02/2022 Many individuals addicted to drugs or alcohol, avoid giving these substances up — because they’re afraid of the withdrawal symptoms associated with detoxing from drugs and alcohol. They may have tried before, but given up as soon...